Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abeykoon, S.*; Howard, C.*; Dominijanni, S.*; Eberhard, L.*; Kurnosov, A.*; Frost, D. J.*; Boffa Ballaran, T.*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Suzuki, Akio*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 128(9), p.e2023JB026710_1 - e2023JB026710_17, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Small amounts of iron sulphide minerals are found in most rocks from the Earth's mantle and as inclusions trapped in natural diamonds. Hydrogen may dissolve into iron sulphide minerals under high pressures and temperature, but is most likely lost once pressure and temperature are removed. In this study, we determined deuterium contents in iron sulphide, held under high pressure and temperature conditions, using neutron diffraction measurements with 6-ram multi-anvil press at PLANET, J-PARC. Deuterium contents in iron sulphide were measured at high-P, up to 11.4 GPa and high-T to 1300 K in in situ neutron diffraction experiments. The total deuterium content increases with both P and T. The results are used to estimate hydrogen contents of iron sulphide minerals in the deep continental lithospheric mantle, which are found to be in the range 1700-2700 ppm. This corresponds to approximately 2-3 ppm of hydrogen in the bulk mantle.
Nakajima, Toru; Kawakami, Tetsuo*; Iwano, Hideki*; Danhara, Toru*; Sakai, Harutaka*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 127(5), p.e2021JB023630_1 - e2021JB023630_33, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.72(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The thermochronological methods were applied to the Higher Himalayan Crystalline (HHC) nappe and the underlying Lesser Himalayan sediments (LHS) to elucidate the denudation process of the middle- and upper-crust of eastern Nepal over the geological time scale. The thermochronological inverse analysis was undertaken for new results of fission-track (FT) age and FT length data of zircon and apatite in order to reconstruct the time-temperature (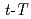 ) paths in the temperature range of 60-350 degree. Eight
) paths in the temperature range of 60-350 degree. Eight 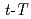 paths obtained along the across-strike section showed that the cooling process of the HHC nappe was characterized by following three aspects: (1) gradual cooling followed by rapid cooling and subsequent gradual cooling, (2) northward-younging of the timing of the rapid cooling, (3) gradual cooling followed by ca. 2 Myr rapid cooling in the frontmost part of the HHC nappe. The observed FT ages and
paths obtained along the across-strike section showed that the cooling process of the HHC nappe was characterized by following three aspects: (1) gradual cooling followed by rapid cooling and subsequent gradual cooling, (2) northward-younging of the timing of the rapid cooling, (3) gradual cooling followed by ca. 2 Myr rapid cooling in the frontmost part of the HHC nappe. The observed FT ages and 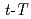 paths were then compared with those predicted by forward thermokinematic modeling. The results of the thermokinematic modeling for the Flat-Ramp-Flat MHT model, in which the HHC and the underlying LHS are denudated accompanied with the movement of the Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT), well reproduced the observed
paths were then compared with those predicted by forward thermokinematic modeling. The results of the thermokinematic modeling for the Flat-Ramp-Flat MHT model, in which the HHC and the underlying LHS are denudated accompanied with the movement of the Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT), well reproduced the observed 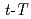 paths and FT ages in eastern Nepal. This suggests that the observed FT ages and
paths and FT ages in eastern Nepal. This suggests that the observed FT ages and 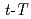 paths reflect a denudation process driven by the movement of the MHT showing the flat-ramp-flat geometry, and that the denudation rate and its spatial distribution have roughly been constant in eastern Nepal since ca. 9 Ma.
paths reflect a denudation process driven by the movement of the MHT showing the flat-ramp-flat geometry, and that the denudation rate and its spatial distribution have roughly been constant in eastern Nepal since ca. 9 Ma.
Usui, Yoichi*; Yamazaki, Toshitsugu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kumagai Yuho*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 124(11), p.10672 - 10686, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:34.06(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We report the discovery of inverse AMS fabrics from pelagic clay recovered by a  12 m long piston core from the western North Pacific. Rock magnetic data and ferromagnetic resonance spectroscopy indicated that magnetofossils account for most of the mean susceptibility regardless of normal or inverse AMS, suggesting that the inverse AMS fabrics due to magnetofossils may be widespread in pelagic clay.
12 m long piston core from the western North Pacific. Rock magnetic data and ferromagnetic resonance spectroscopy indicated that magnetofossils account for most of the mean susceptibility regardless of normal or inverse AMS, suggesting that the inverse AMS fabrics due to magnetofossils may be widespread in pelagic clay.
Sueoka, Shigeru; Ikeda, Yasutaka*; Kano, Kenichi*; Tsutsumi, Hiroyuki*; Tagami, Takahiro*; Kohn, B. P.*; Hasebe, Noriko*; Tamura, Akihiro*; Arai, Shoji*; Shibata, Kenji*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 122(8), p.6787 - 6810, 2017/08
no abstracts in English
Sueoka, Shigeru; Shimada, Koji; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Niwa, Masakazu; Yasue, Kenichi; Umeda, Koji*; Danhara, Toru*; Iwano, Hideki*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 122(3), p.1848 - 1859, 2017/03
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Eiichi
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 121(1), p.70 - 91, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:70.61(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Macroscopic failure modes (extensional failure or shear failure) in fault damage zones influence hydrogeological properties of fault zones. Based on the Griffith-Coulomb criterion and a simple assumption that the failures are predominantly induced by increasing of differential stresses and/or decreasing of effective normal stresses due to stress concentration along faults, it is implied that extension fractures can exclusively propagate from the faults when the effective mean stress is less than twice the rock tensile strength, whereas shear fractures also can develop when the effective mean stress is more than twice the rock tensile strength, which suppresses the formation of extension fractures. In this study, mechanical tests (the undrained triaxial tests and the unconfined compressive strength tests) using siliceous mudstone specimens given artificial fault(s) were performed under multiple effective confining pressures. Comparison between the damage zone fractures formed at the fault tips by the tests and the loaded effective mean stresses provided results consistent with the above simple model. The similar results are also suggested from the occurrence of natural damage zone fractures observed in the same siliceous mudstone by core logging. Laboratory-measured tensile strengths could be used as the lower threshold strengths considering the strain rate and scale effects and it is implied that hard-linked highly permeable fault zones involving many extension fractures are limited to rock domains which have experienced the effective mean stress less than twice the tensile strength.
Umeda, Koji; Asamori, Koichi; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Kobori, Kazuo; Hama, Yuki*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 120(4), p.2279 - 2291, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.07(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Following the Mw 9.0 Tohoku-Oki earthquake, an unusual, shallow normal-faulting swarm sequence occurred near the Pacific coast in the southeast Tohoku district. The observed  He/
He/ He ratios are significantly lower than the atmospheric value, indicating mantle helium contributed less than 10%. The plausible source of fluids can be attributed to waters released owing to sediment porosity collapse, and smectite-illite and opal-quartz reactions in the subducting sediments, rather than dehydration reactions of the subducting altered basalts and/or hydrated mantle. The aqueous fluids driven off the subducting slab migrate into the fore-arc crust, because of the pressure gradient between lithostatic pore pressure along the plate interface and hydrostatic pore pressure in the overriding crust. The swarm earthquake sequence would have been triggered by stress change associated with the Tohoku-Oki earthquake, enhanced by fluid flow along inherited weakened zones in the crust.
He ratios are significantly lower than the atmospheric value, indicating mantle helium contributed less than 10%. The plausible source of fluids can be attributed to waters released owing to sediment porosity collapse, and smectite-illite and opal-quartz reactions in the subducting sediments, rather than dehydration reactions of the subducting altered basalts and/or hydrated mantle. The aqueous fluids driven off the subducting slab migrate into the fore-arc crust, because of the pressure gradient between lithostatic pore pressure along the plate interface and hydrostatic pore pressure in the overriding crust. The swarm earthquake sequence would have been triggered by stress change associated with the Tohoku-Oki earthquake, enhanced by fluid flow along inherited weakened zones in the crust.
Ishii, Eiichi
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 120(4), p.2220 - 2241, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:24.32(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The author shows a clear correlation with negative power law between transmissivities along fluid-conductive fault zones detected by fluid loggings in boreholes and the effective mean stress normalized a tensile strength of the rock, using data sets from six sites in different conditions. The obtained empirical relation allows to spatially and temporally predicting transmissivities along possible fluid-conductive fault zones in the upper crust using the normalized stress, providing a very useful benchmark for many geoscientific and geotechnical problems relevant to fault zone permeability.
 He/
He/ He ratios and subduction of the Philippine Sea plate beneath southwest Japan
He ratios and subduction of the Philippine Sea plate beneath southwest JapanUmeda, Koji; Kusano, Tomohiro; Asamori, Koichi; McCrank, G. F.*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 117(B10), p.B10204_1 - B10204_13, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.04(Geochemistry & Geophysics)In order to elucidate the geographic distribution of  He/
He/ He ratios in Southwest Japan, the data from a total of 924 sites were compiled and synthesized. There appears to be good correlation between variations in mantle helium and the geophysical evidence indicating the configuration of the subducting Philippine Sea plate. The helium isotopes observed on the Earth's surface may be efficient geochemical indicators of the configuration of a relatively younger, warm aseismic slab, especially useful in seismically inactive areas.
He ratios in Southwest Japan, the data from a total of 924 sites were compiled and synthesized. There appears to be good correlation between variations in mantle helium and the geophysical evidence indicating the configuration of the subducting Philippine Sea plate. The helium isotopes observed on the Earth's surface may be efficient geochemical indicators of the configuration of a relatively younger, warm aseismic slab, especially useful in seismically inactive areas.
Ishii, Eiichi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Funaki, Hironori; Sugita, Yutaka; Kurikami, Hiroshi
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 116(B09), p.B09206_1 - B09206_15, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:72.08(Geochemistry & Geophysics)This paper addresses relationship among brittleness, deformation behavior, and transport properties of mudstones at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory site, Japan. The mudstones include indurated/cemented rocks by silica diagenesis. The geological, mechanical and hydrogeological data were systematically interpreted using a brittleness index (BRI) concept which is defined using unconfined compressive strength and the unconfined compressive strength of a normally consolidated rock in non-overpressured domains.
Martin, A. J.*; Umeda, Koji; Conner, C. B.*; Weller, J. N.*; Zhao, D.*; Takahashi, Masaki*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 109(B10), p.B10208_1 - B10208_20, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:73.16(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We achieve this using Bayesian inference in order to combine one or more sets of information (geophysical data) to a priori assumptions of volcano spatio-temporal distributions yielding modified a posteriori probabilities.
King, C.-Y.; Azuma, S.; Igarashi, G.; Saito, Hiroshi; Wakita, H.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 104(B6), p.13073 - 13082, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:102 Percentile:86.35(Geochemistry & Geophysics)None